“It Is So Loud Inside My Head”
“It is so loud inside my head. It feels like electrical impulses are going through my head all the time. If you took that pen and tapped it on the table I can feel it all the way down my spinal column. It is so loud inside my head.”
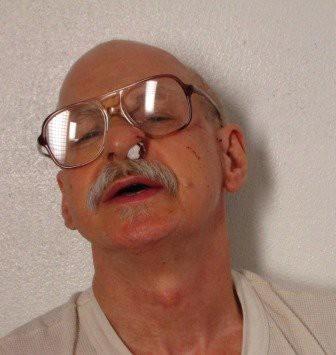
“It is so loud inside my head. It feels like electrical impulses are going through my head all the time. If you took that pen and tapped it on the table I can feel it all the way down my spinal column. It is so loud inside my head.”
Those are Jack Greene’s words. He is the 62-year-old man that the state of Arkansas hopes to execute on November 9th for the 1991 killing of Sidney Burnett. Greene suffers from crippling psychiatric deficits, a possible intellectual disability, and a mental illness so severe that there are questions about his competency. He received such grossly inadequate representation at trial that the jury that sentenced him to death never heard of his devastating mental illness — a refrain all too familiar in capital cases. The state is aware of the glaring problems in Greene’s case, but it still hopes to execute him next month.
Greene, for example, regularly stuffs his ears and nose with paper “to alleviate perceived (but delusional) injuries.” Sometimes he intentionally causes his nose to bleed, and guards discover his face covered with blood. He eats out of his sink; his toilet is his desk. He thinks his central nervous system is totally destroyed, caused by, in his words,
[t]he prolong and repeated injuries on me . . . by staff of the Ark. Dept. of Corrections with the deliberate permanent destruction of such vital bodily functioning organs that’s caused injuries so severe and traumaticly [sic] inflicted to my brain, head, left inner ear, etc. . . . for all of which is so painfully torturing and inhumane I can no longer humanly function properly and live with.
He believes that his ex-attorney, the prison warden, a nurse, and a prison guard have conspired together (in that “chronological order”) to destroy “these vital functioning organs,” and that they are also preventing him from being extradited to North Carolina, where he could receive adequate medical care. He thinks his looming execution is part of this conspiracy.
Doctors believe Greene has organic brain damage. He has had a serious head injury in the past, and neuropsychological testing reveals damage to his frontal lobes. Several experts who have examined him have diagnosed him with a psychotic disorder, and his current lawyers are certain he is not competent to be executed. He also might be intellectually disabled, a status that, like incompetence, would render him categorically ineligible for the death penalty.
Then there is the trauma and the familial mental illness visible in many of Greene’s relatives. Greene’s father killed himself when Greene was an infant. His mother would later overdose on pain pills, and his brother later shot himself. Greene’s grandfather physically abused him and his siblings, sometimes rubbing salt in the wounds he caused. Greene lived in a house with no running water, electricity, or plumbing. At eleven, his grandfather handed him over to a notorious state-run training school for boys. While there, Greene was sexually and physically abused.
The evidence described above is the type that often causes juries to spare someone’s life, according to the findings of the Capital Jury Project. But at Greene’s sentencing trial, his attorney did not put on a mental-health expert and he presented no other mental-health evidence, although the signs of his illness were readily apparent. Instead, to convince the jury to spare Greene’s life, his lawyer presented a measly 46 pages of testimony, 33 of which were read from a cold, emotionless, transcript from a prior proceeding.
What happened next is equally disturbing. During post-conviction proceedings, an expert found that Greene might be intellectually disabled but stated that he needed to do additional testing to confirm. Greene, insistent that his lawyers were conspiring to torture him, asked the district court to withdraw the claim. He accused the Federal Defender’s Office of “making [him] out to be some kind of incompetent retard to get their office appointed to [his] case and try and cover up crimes of inhumane injuries maim and torture.” The judge found Greene competent to abandon this potentially life-saving claim and withdrew it. No court has ever heard it.
Perhaps the most shocking thing in Mr. Greene’s case is that, with a little more than two weeks until the scheduled execution, he has yet to receive a hearing to determine whether he is competent for execution under U.S. Supreme Court precedent that bars the execution of persons who lack a rational understanding of the punishment they are to receive. Arkansas’s unusual statute gives the Director of the Department of Correction sole discretion in making competency determinations. This means that the same person who is in charge of carrying out Mr. Greene’s execution also gets to determine –without a fair and independent court hearing — if he is competent for execution.
If the state has its way, Jack Greene will join a group of four other men executed by Arkansas in 2017, a group that to a man suffered from the most debilitating illnesses and trauma and received the worst lawyers. Ledell Lee, who might have been intellectually disabled, had lawyers who tried to withdraw from his case, citing a “gross [ethical] conflict,” a drunk lawyer, a mentally ill lawyer, but never, until it was too late, a competent lawyer. Marcel Wayne Williams had a mother who pimped him out for sex at ten and who tortured him by pouring boiling water on him and covering him with tar; Kenneth Williams may well have been intellectually disabled; and Jack Jones suffered from extreme physical abuse, was brutally raped by strangers, and suffered from bipolar disorder. Juries never heard these stories because of ineffective lawyering.
What is happening in Arkansas is a stain on our country’s moral conscience. Under the Eighth Amendment, the death penalty is supposed to be reserved for the worst of the worst, society’s most culpable. The prosecutors’ continued push for death in the face of severe illness and trauma, never heard about by juries, flouts that constitutional promise. And each time a court allows a state to carry out the harshest of punishments on the most impaired and least represented, it mocks the promise of justice. Will a court finally recognize this reality and intervene? Or will Greene become another tragedy in a system that is completely and utterly broken?
